Probiotics: The Good Bacteria
Probiotics are living microorganisms that can provide health benefits such as supporting gut and immune health and contributing to the maintenance of a balanced gut environment. This is important for the proper functioning of the digestive system and the entire body. They also help defend the body from infections caused by bad bacteria or other germs. Many people think that taking probiotic pills or supplements will keep them healthy. However, probiotics actually get into your body on their own, so your body is always maintaining your “good bacteria” without you doing or taking anything extra. Probiotics may be helpful if you have certain conditions and we’ll talk about when they may be useful to take as well as how to choose which probiotic may be the most beneficial for you.
Sources of Probiotics
Probiotics are often found in fermented foods. Some of the most common food sources of probiotics include: yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, tempeh, kimchi, miso, kombucha, pickles, traditional buttermilk, natto, and some types of cheese. If you consume any of these foods on a regular basis, it’s not recommended that you also take a probiotic supplement.
Probiotic Use
The decision to use a probiotic should first be discussed between you and your doctor to ensure you will benefit from taking a probiotic. Although probiotics are rarely considered to be harmful, unless you have a certain medical condition, there is no proven benefit of taking probiotics. Researchers are currently studying the use of probiotics for:
- Helping fight or prevent infections in the stomach, including a serious infections like C. difficile and H. pylori
- Helping with diarrhea, constipation, and some conditions that cause these symptoms such as irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease and antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Preventing or treating allergies, including a skin condition called eczema
- Helping prevent or fight infections in the vagina
- Helping lower blood sugar in diabetes
- Helping lower lipid levels in cardiovascular disease
If you have one of these conditions listed above and would be interested in starting a probiotic, make sure you have a conversation with your doctor before you start taking one. If you don’t have one of these conditions, it’s recommended to not use a probiotic. If you are worried about your gut health, make sure you are implementing a healthy diet with some of the foods listed above to create a healthy lifestyle and good digestion. Additionally, probiotics are not recommended for patients with weakened immune systems.
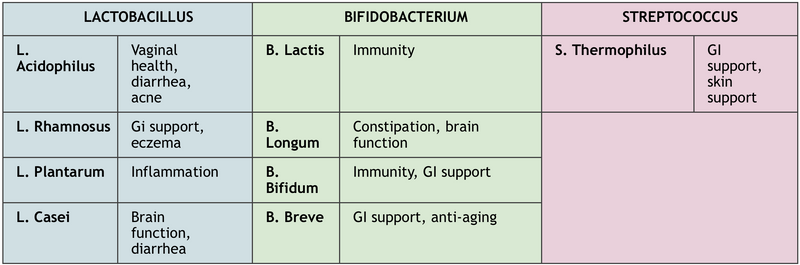
Types of Probiotics
There are many different “strains” of probiotics that contain various types of bacteria. More research needs to be done on the specific strains and their effects on the body. If you are trying to find the right probiotic, look for the right strain and choose the product that will benefit you based on what you would like to use it for. Here is a helpful table that outlines the strains, types of bacteria and where they help in your body: